Deep dive into AI in the Legal Profession: A Comprehensive Guide

In today's fast-paced world, the legal profession, not unlike others, is constantly evolving to keep up, and the adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a game-changer. Conga explores the intricacies of AI technology and its applications within the legal sector. From understanding AI types to how it's trained and what you can expect from it, this article will delve into the realm of AI and the potential for how it can significantly impact legal teams.
What is AI?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is the term used to describe how computers and other technologies simulate human intelligence. It encompasses the development of algorithms and systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as problem-solving, reasoning, learning from data, understanding natural language, recognizing patterns, and making decisions.
Types of AI Technologies
Within the AI umbrella, there are several different types of technologies used and here are some of those terms:
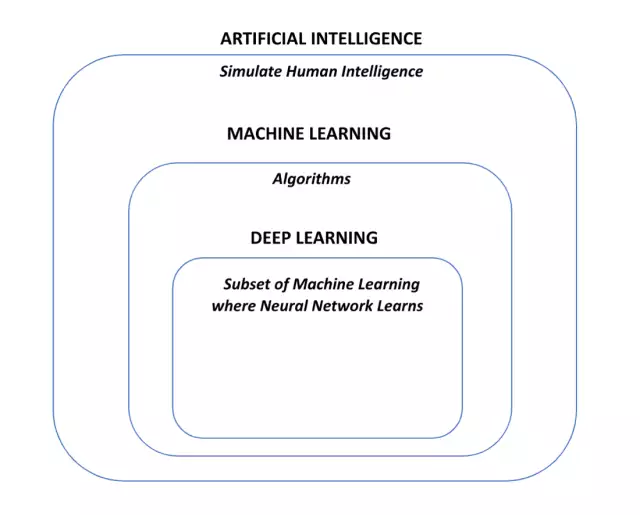
- Machine Learning (ML): ML involves training computers to learn from data, improving their performance on tasks without explicit programming. Supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning are various types of ML.
- Deep Learning: A subset of ML, deep learning utilizes deep neural networks with multiple layers, significantly enhancing tasks like speech and image recognition.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP aims to enable computers to comprehend, analyze, and generate human language. Applications utilizing NLP include sentiment analysis, language translation, and chatbots. In the context of contracts, NLP can classify text as specific clauses and detect fields like contract dates. Typically, Large Language Models (LLM) with millions of parameters are applied for solving NLP problems. These LLMs are trained using Deep Learning.
- Computer Vision: Computer vision focuses on teaching computers to perceive and understand visual data, such as images and videos. Applications include autonomous vehicles, object detection, and facial recognition. For example, with contracts Computer Vision techniques are used to identify table structures and cells.
- Generative AI (GenAI): GenAI, like LLMs (Large Language Models) such as GPT-4 and ChatGPT-3.5, produces original content and analyze existing content.
Generative AI vs. Traditional AI
Traditional AI, also known as Narrow AI or Weak AI, is designed to carry out specific, individualized tasks and creates systems that react to a specific set of inputs. These systems learn from the data and base choices or predictions on the analysis of the data. GenAI, on the other hand, produces new data that is comparable to its training data, making it valuable for creating new content like summaries, descriptions or stories. It can also analyze prompts and data.
Is one form or type of AI technology better than another?
GenAI can be used to solve many problems very quickly by building an initial prototype, however it can suffer from Hallucination. The term "GenAI Hallucination" describes situations in which GenAI models create conclusions or results that are seen as "false" or "nonsensical." The intricacy of language and a lack of data or context are two potential reasons ChatGPT can hallucinate. ChatGPT is also trained on data only up to 2021, so it will hallucinate about anything after that date as well. On the other hand, Traditional AI works very well in a closed domain for a specific predetermined task but struggles in the generation of new content. Both have their pros and cons, and at Conga, we embrace a hybrid approach, leveraging the strengths of both to benefit our clients.
How Does AI Work in Legal Teams?
AI isn’t new to the legal profession. It’s been utilized in e-discovery for more than two decades. AI's integration into how to manage contracts, however, has paved the way for a transformative shift in the way legal professionals manage their transactional work. Here, we delve deeper into how AI operates within legal teams, offering insights into its functionalities and potential benefits.
Data Encoding and Training:
At the heart of AI's functionality lies the process of data encoding and training. To enable machines to understand language or images, this involves converting complex information into machine-understandable formats, such as vectors. Vector embeddings are a way to convert words and sentences and other data into numbers that capture their meaning and relationships. When AI is trained for a specific task, it learns the underlying patterns in the data.
For example, let's consider the task of classifying a paragraph within a contract as a specific clause, like "Governing Law." AI algorithms are exposed to a vast corpus of contract documents during the training phase. They analyze the text's structure, keywords, and context, including the proximity of certain words to one another, discerning patterns that differentiate the various clauses. Once trained, the AI can accurately classify similar paragraphs, saving valuable time for legal professionals.
Prediction Based on Learning:
Once AI has undergone the training process, it can predict outcomes or perform tasks based on the patterns it has learned. In the context of legal teams, this prediction capability can be a game-changer. Here's how it works:
- Contract Classification: AI can swiftly categorize contracts into different types, such as Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), Master Service Agreements (MSAs), and more. This classification ensures that legal professionals can quickly locate and manage relevant documents.
- Clause Classification: AI can identify and extract specific clauses within contracts, such as indemnification or force majeure clauses. This capability streamlines contract analysis and due diligence processes.
- Field Prediction: For Legal, AI can predict values based on the patterns it recognizes within documents. This predictive ability aids in accurate financial analysis and budgeting.
- Automatic Clause Library Creation: AI can analyze a set of documents, grouping similar clauses together and identifying the most used language. This feature is particularly useful for efficiently creating standardized clause libraries, ensuring consistent language is used across contracts, and saving a lot of time in setting it up.
- Risk and Redlining: AI can assist in identifying risky language within contracts, enabling legal professionals to focus on critical clauses that require prioritized attention.
- Visual Intelligence: AI's capabilities extend beyond text to visual elements within documents. It can identify layout-based elements like tables, columns, rows, and cells. This visual intelligence is valuable for extracting structured data from unstructured documents for things such as a price list or discounting table in a contract
Aids Accuracy and Efficiency
The integration of AI in legal teams is not just about automation; it's about enhancing efficiency. AI can analyze vast volumes of legal documents in a fraction of the time it would take a human, reducing the amount of time needed for human review.
Furthermore, AI operates tirelessly, 24/7, ensuring that legal professionals can access critical information and insights whenever they need them. This continuous support allows legal teams to focus their human expertise on higher-value tasks, such as legal strategy, negotiation, and client interactions. For the AI technology to be successful in its predictions and content generation, it does require a lot of training (in volume, velocity and volume of data samples) and benefits from consistent feedback. This helps it to adapt to changing data patterns and discover new insights.
The term “human-in-the-loop" is typically used to describe leveraging experts to aid in the review of the AI predictions to minimize errors and oversee the machine's learning process. These individuals possess expertise in several domains, including data annotation, quality assurance, data science, and machine learning engineering, potentially serving as vendors in their respective fields, such as legal professionals in the case of contract AI review. One potential approach to address the concern of hallucinations with the use of GenAI, as mentioned earlier, is to limit its use to areas where absolute precision is not essential. Or, an alternative strategy is to embrace a collaborative relationship between AI and human connection.
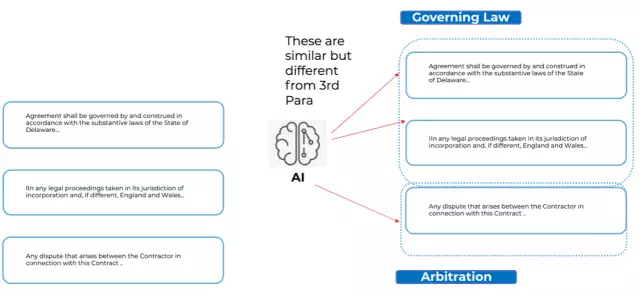
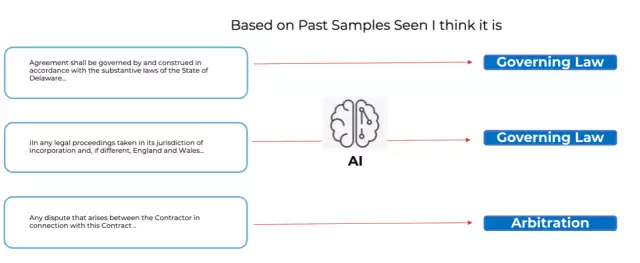
In conclusion, AI technology is revolutionizing legal operations by enhancing productivity and streamlining complex processes. Conga's Revenue Lifecycle Cloud harnesses the power of AI functionality to eliminate manual tasks, improve revenue predictability, and provide exceptional results for legal teams to operate in harmony and coordination with other business units and stakeholders in the revenue lifecycle of the business. To learn more about how Conga can transform your legal operations, book a demo with us today. Discover the future of legal technology with Conga solutions.



